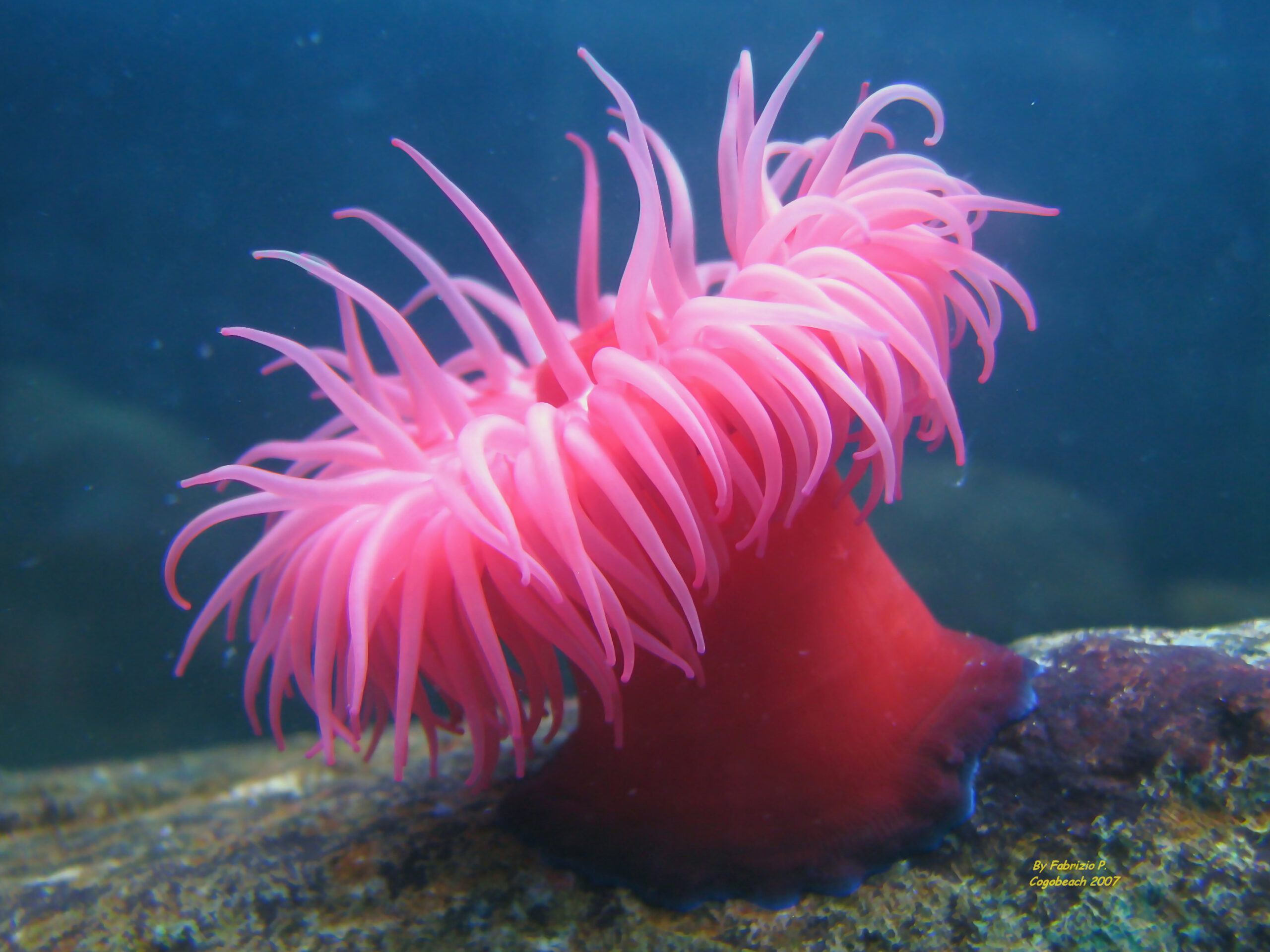
Beadlet Anemone (Actinia equina)

Beadlet Anemone (Actinia equina) - Zeeanemoon
- Taxonomy: The Beadlet Anemone belongs to the Actiniidae family. This family includes various anemones with distinctive shapes and colors.
- Species: The Beadlet Anemone is one of the most common species found along the coasts of Europe. It can reach a height of about 10 cm.
- Habitat: These anemones are typically found in tidal pools and on rocky substrates. They thrive in intertidal zones. Where they can withstand changing water levels.
- Diet: Beadlet Anemones are carnivorous. They feed on small fish, crustaceans, and plankton. They use their stinging tentacles to capture prey.
- Reproduction: They can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction occurs through budding. Sexual reproduction involves releasing eggs and sperm into the water.
- Unique Features: These anemones have a unique ability to retract their tentacles when exposed to air. This helps them conserve moisture and avoid desiccation.
- Color Variation: They can change color based on environmental conditions. Typically, they appear in shades of green, brown, or red.
- Lifespan: In the wild, Beadlet Anemones can live for several years, with some estimates reaching up to 50 years.
Beadlet Anemone: The Resilient Beauty of the Shore
When we think of vibrant marine life, images of colorful fish and graceful sea turtles often come to mind. However, one creature that deserves our attention is the Beadlet Anemone. This remarkable sea creature is a symbol of resilience and beauty, often overlooked yet vital to its ecosystem.
What is a Beadlet Anemone?
The Beadlet Anemone, known scientifically as Actinia equina, is a marine invertebrate found in coastal waters. Its distinctive shape resembles a small, colorful blob. These anemones can attach themselves to rocks and surfaces using a specialized foot. They have a crown of tentacles surrounding their central mouth. The tentacles are equipped with nematocysts, which allow them to capture prey and defend against predators.
A Day in the Life of a Beadlet Anemone
During high tide, Beadlet Anemones are submerged in water. They expand their tentacles to feed on passing plankton and small fish. As the tide recedes, they retract their tentacles to conserve moisture. This ability to retract is crucial for survival in intertidal zones where exposure to air is common.
Unique Reproduction: A Dual Approach
Beadlet Anemones have a fascinating reproductive strategy. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In sexual reproduction, males and females release their gametes into the water. Fertilized eggs develop into free-swimming larvae that eventually settle and grow into new anemones. Asexual reproduction occurs through budding, allowing them to increase their numbers rapidly.
Ecological Role: Essential for Biodiversity
Though small, Beadlet Anemones play a significant role in their habitats. They provide food for various marine species. Their presence helps maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Additionally, they offer shelter to small fish and invertebrates, enhancing biodiversity in rocky tidal pools.
Conclusion
The Beadlet Anemone is a testament to the beauty and resilience of marine life. With their unique adaptations, fascinating reproduction, and vital ecological role, they deserve our respect and protection. Next time you explore the shore, take a moment to appreciate these remarkable creatures that thrive in the tide pools. They remind us of the intricate web of life beneath the waves.